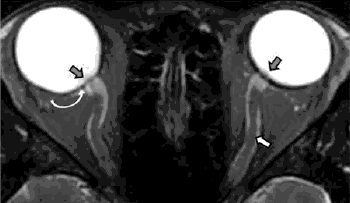
Questions:
1. What specific steps should be followed in examining a patient with anisocoria?
2. What are the characteristics of physiologic anisocoria?
3. What are the ocular causes of anisocoria?
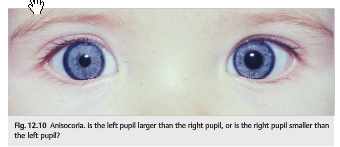
Questions:
1. What specific steps should be followed in examining a patient with anisocoria?
2. What are the characteristics of physiologic anisocoria?
3. What are the ocular causes of anisocoria?

Questions:
1. When examining the pupils, what should you record?
2. Does a RAPD cause anisocoria?
3. If a patient is suspected of having optic neuropathy (regardless of the cause) has no RAPD does that rule-out this diagnosis?
4. If a patient has a severe bilateral optic neuropathy will the pupils respond to near stimuli?
5. Which order neuron is involved when the Horner syndrome is caused by a tumor in the apex of a lung?
6. Why do patients with a third-order Horner syndrome usually do not have anhidrosis?
7. What is neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular junction of the iris sphincter to result in pupillary constriction?
8. What is neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular junction of the iris sphincter to result in pupillary dilation?
9. Why do lesions of the geniculate nucleus, the optic radiations, or the visual cortex not affect pupillary size or pupillary reactivity?
10. What is the course of the parasympathetic fibers for pupillary constriction from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus to the ciliary ganglion?
11. What is the ratio of postganglionic parasympathetic fibers that innervate the ciliary muscle to those that innervate the pupillary sphincter muscle?
Questions:
1. What is the classic tetrad of narcolepsy?
2. What is palinopsia?
3. What is polyopia?
4. What is the Alice in Wonderland syndrome?
5. What is visual allesthesia?
6. What is the Riddoch Phenomenon?
7. What is Blindsight?
8. What is Residual Vision?
9. What 6 conditions are associated oscillopsia?
10. What is the Anton Syndrome?
Neuro-ophthalmology Question of the Week: Hallucinations and Illusions 1
Questions:
1. What is the difference between a hallucination and an illusion?
2. Are isolated visual hallucinations common in psychiatric disorders?
3. What is the Pulfrich effect?
4. What is the Charles Bonnet syndrome?
5. Which dementias may be associated with paranoid hallucinations and illusions?
6. What is the duration of migraine with visual aura episodes?
7. What is the duration of visual phenomenon of occipital seizures?
8. What is peduncular hallucinosis and where is its lesion?
Questions:
1. What is the Balint syndrome and where is its lesion?
2. What is the Gerstmann syndrome and where is its lesion?
3. What is hemineglect and where is its lesion?
4. What are the symptoms of posterior cortical atrophy and where is its lesion?
5. What are the visual symptoms of Alzheimer disease and when in the course of the disease are they likely to occur?
6. What visual symptoms may occur in Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease?
Questions:
1. What are the names and functions of the 2 visual higher cortical function processing streams?
2. What are the findings in a patient with alexia without agraphia?
3. Where is the lesion in alexia without agraphia?
4. What is prosopagnosia?
5. What is visual object agnosia?
6. What is optic aphasia?
7. What is topographagnosia?
8. What is akinetopsia?
9. What is simultagnosia?
10. What is ocular apraxia?
Questions:
1. What are the symptoms of IIH?
2. What are the criteria for the diagnosis of IIH?
3. What is the ideal test when evaluating a patient with presumed papilledema?
4. A patient with papilledema has a normal brain MRI, what test should be done next?
5. What should one consider if the headaches of IIH do not improve (at least transiently) after lumbar puncture?
6. What does a normal Brain MRI in the setting of papilledema suggest?
7. What should be evaluated next in a patient with bilateral swollen discs, normal BP, normal CT with and without contrast, LP opening pressure >250mm and normal or abnormal CSF contents?
8. What should be evaluated next in a patient with bilateral swollen discs, normal BP, normal MRI with and without contrast, LP opening pressure >250mm and normal or abnormal CSF contents?
9. What are the main factors associated with IIH?
10. What condition can cerebral venous thrombosis mimic?
11. What can early recognition of cerebral venous thrombosis prevent?
12. Should papilledema from a meningeal process or cerebral venous thrombosis be classified as IIH?
13. What are the goals of the management of IIH?
14. What is basis for management of IIH?
15. What MRI findings are supportive of the diagnosis of IIH?