Question: Which of the following are good indications for CT and which for MRI?
1 Bone lesions
2 Brain lesions
3 Chiasmal syndrome
4 Fungal sinusitis
5 Infectious or noninfectious orbital inflammation
6 Lacrimal gland lesions
7 Lesions that may contain calcium
8 Ocular trauma to rule out a foreign body
9 Optic neuropathy
10 Orbital apex or cavernous sinus syndrome
11 Orbital trauma
12 Preoperative imaging for orbital disease when imaging of the facial sinuses is very important
13 Suspected optic nerve tumor
14 Wooden foreign body
Archives for April 2017
Neuro-ophthalmology Question of the Week: Neuroimaging
Neuro-ophthalmology Question of the Week: B-scan Ultrasound
Question: What are 7 indications for B-scan echography?
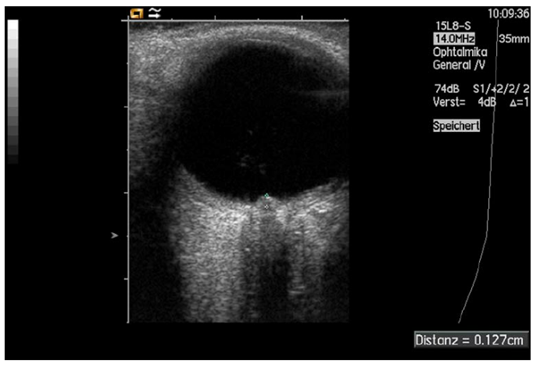
Fig. 8. Measurement of papilledema using ultrasound: disc elevation is quantified by putting the first caliper on the uppermost part of the swollen disc; the second caliper is positioned on the strongly reflecting line representing the lamina cribrosa 8
Neuro-ophthalmology Question of the Week: Fundus Autofluorescence
Question: Which of the following are hyperautofluorescent?
1. Optic Disc Drusen
2. Papilledema
3. Accumulation of lipofuscin in the retinal pigment epithelium
4. Loss of lipofuscin in the retinal pigment epithelium
5. Central serous chorioretinopathy
6. Best disease
 1
1
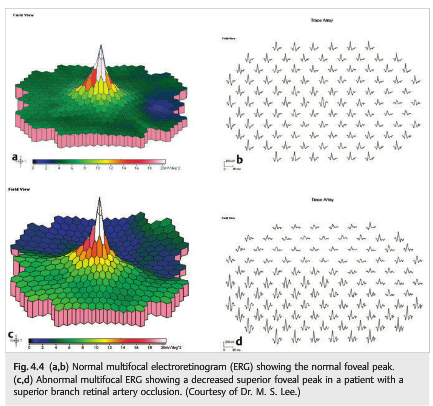
Neuro-ophthalmology Question of the Week: Electroretinography
Which of the following statements are correct?
1. Full-field ERG is useful in detecting diffuse retinal disease in the setting of generalized or peripheral vision loss.
2. The ERG is invariably severely depressed by the time patients complain of visual loss.
3. In full-field ERG the responses cannot be substantially altered voluntarily.
4. The full-field ERG may be normal in minor or localized retinal disease, particularly maculopathies, even with severe visual acuity loss.
5. Multifocal ERG is extremely helpful in detecting occult focal retinal abnormalities within the macula.
6. Uncooperative patients can alter the responses on a multifocal ERG by not fixating accurately.