Questions:
1. What historical factors are important to assess in a patient with suspected optic neuropathy?
2. What tests should be considered based on the assessment of appropriate historical factors?
 1
1
Questions:
1. What historical factors are important to assess in a patient with suspected optic neuropathy?
2. What tests should be considered based on the assessment of appropriate historical factors?
 1
1
Questions:
1. Are some maculopathies associated with mild optic nerve pallor?
2. Can maculopathies have dyschromatopsia?
3. In evaluating optic neuritis, when should a lumbar puncture for CSF analysis be considered?
Fig.8.5
(a) Isolated right inflammatory optic neuropathy. There is a large central scotoma seen as diffuse depression on a 24–2 Humphrey visual field test.
(b)Coronal and axial T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with fat suppression and contrast showing enhancement of the orbital portion of the right optic nerve(arrow).
Question:
1. In acute optic neuropathy, how long after onset does the optic nerve head become pale?
2. When is electrophysiologic testing useful in acute optic neuropathies?
3. What does a painful orbital apex syndrome in a diabetic patient suggest?
 Fig.8.1
Fig.8.1
Questions:
 1
1
Questions:
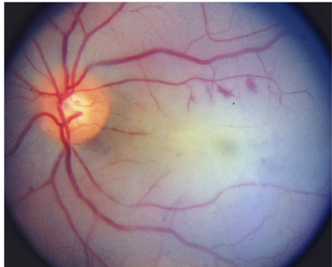
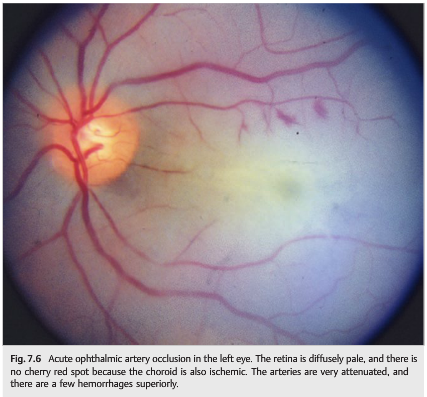
1. What should be done for a patient with monocular vision loss, not due to nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, or other ophthalmologic disease, but with branch or central retinal artery occlusions or amaurosis fugax?
2. What should be considered if a central artery is associated with pain?
3. What is the most common cause of ophthalmic artery occlusion?
4. What are the findings from ophthalmic artery occlusion
5. What finding seen in acute central artery occlusion is not seen with acute ophthalmic artery occlusion?
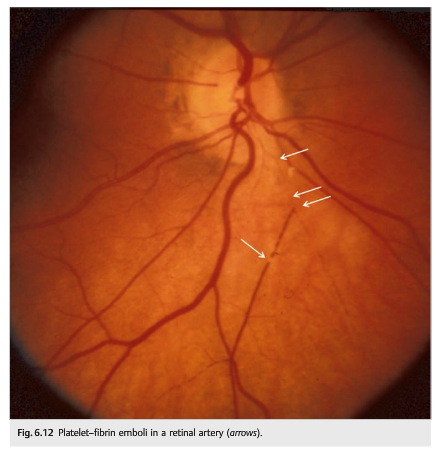
6. What work-up should be done when retinal emboli are found in an asymptomatic patient?
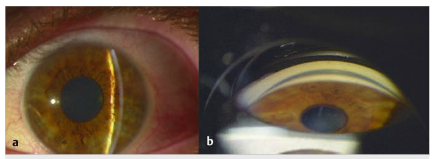
7. What is the appearance of cholesterol emboli?
8. What are common sources for cholesterol emboli?
9. What is the appearance of talc emboli?
10. What condition is associated with talc emboli?
11. In a patient with acute retinal ischemia what tests should be ordered for thrombophilia?
 1
1
A 52-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a 1-year history of headache and reduced visual acuity. Physical examination showed seesaw nystagmus; a …
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMicm1613244#t=article
Question: What are 5 categories of symptoms that help differentiate the 3 most common causes of binocular transient vision loss (migraine visual aura, occipital transient ischemic attacks, and occipital seizures)?
 1
1
Questions:
1. What should be done immediately when a patient presents with a recent vascular TMVL?
2. What should be done emergently in the presence of an acute central retinal artery or branch retinal artery occlusion?
3. What is the chance and timeline of stroke after TMVL in the presence of ipsilateral atheromatous internal carotid stenosis ≥50%?
4. What is the yearly risk of vascular death (myocardial infarction) in patients with TMVL and atheromatous disease?
 1
1
Neuro-ophthalmology Question of the Week: Transient Monocular Vision Loss Categories
Question: What are the three main categories of transient monocular vision loss?
 1
1
Questions:
1. What is the preferred term for abrupt and temporary visual loss in one eye?
2. What is the most common cause of transient monocular vision loss?
3. What is amaurosis fugax?
 1
1