Question: When should an ophthalmologist consider the diagnosis of a paraneoplastic syndrome?
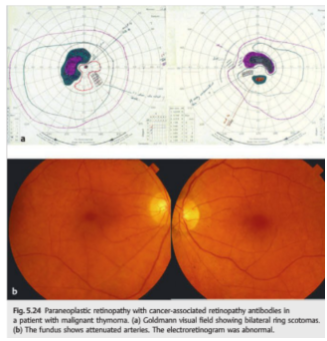 2
2
Question with answers: When should an ophthalmologist consider the diagnosis of a paraneoplastic syndrome?
“In terms of afferent symptoms, an unexplained, painless, progressive vision loss is typical. With retinal involvement, there may be photopsias, night blindness, or ring scotomas. In the optic neuropathies, there is most commonly bilateral disc swelling often accompanied by vitritis. Efferent symptoms include myasthenic-like presentation or the presence of opsoclonus/myoclonus syndrome (OMS).”1
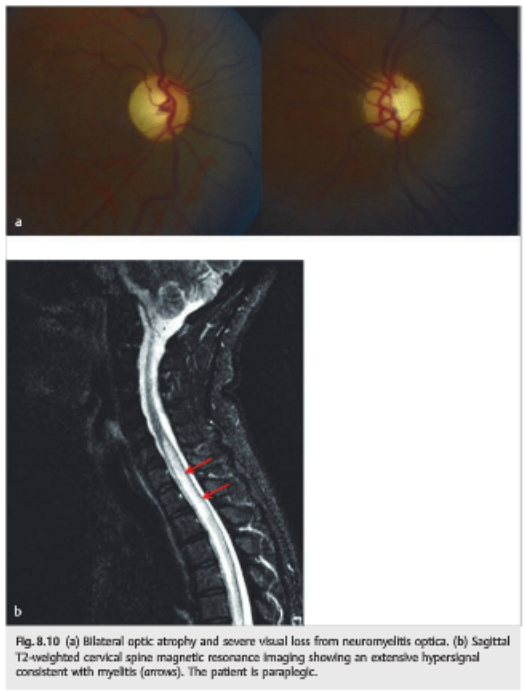 3
3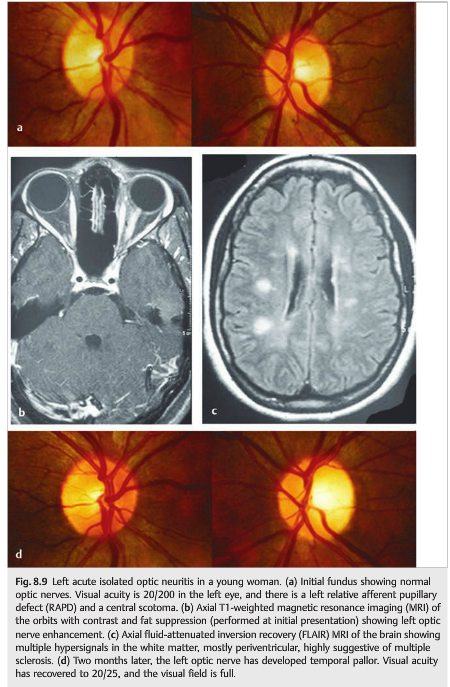
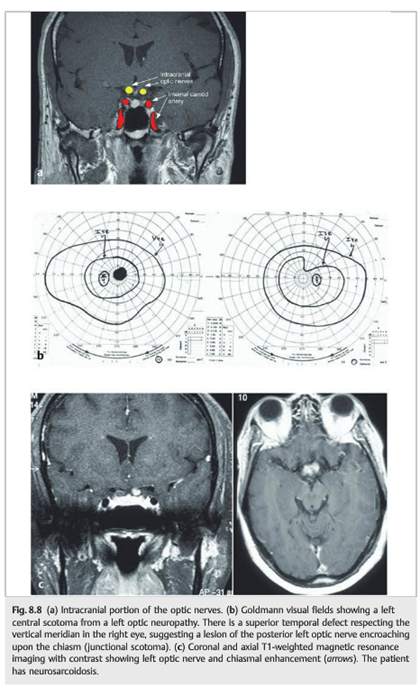 1
1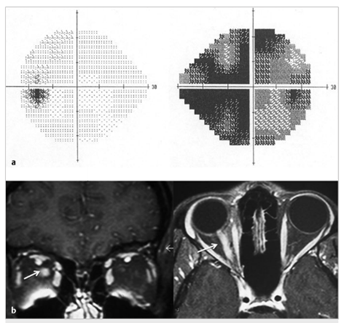
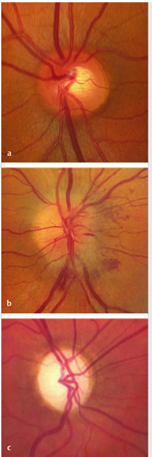 Fig.8.1
Fig.8.1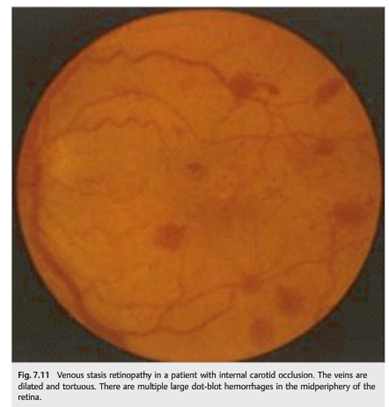 1
1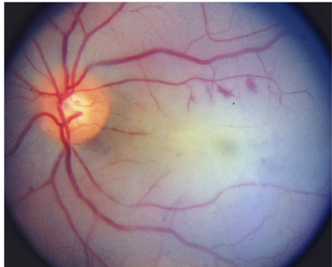 1
1